 User's Guide
User's Guide  Part II. Tutorials
Part II. Tutorials Chapter 12. Introduction to Subqueries
Chapter 12. Introduction to SubqueriesSuppose you need a chronological list of orders and the company that placed them, but would like the company name instead of their customer ID. You can get this result using a join as follows:
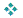 To list the order id, date, and company name for each order since the beginning of 1994:
To list the order id, date, and company name for each order since the beginning of 1994:
SELECT sales_order.id,sales_order.order_date,customer.company_nameFROM sales_orderKEY JOIN customerWHERE order_date > '1994/01/01'ORDER BY order_date
| id | order_date | company_name |
|---|---|---|
| 2473 | 1994-01-04 | Peachtree Active Wear |
| 2474 | 1994-01-04 | Sampson & Sons |
| 2036 | 1994-01-05 | Hermanns |
| 2106 | 1994-01-05 | Salt & Pepper's |
| 2475 | 1994-01-05 | Cinnamon Rainbow's |
The following statement obtains the same results using a subquery instead of a join:
SELECT sales_order.id,sales_order.order_date,( SELECT company_name FROM customerWHERE customer.id = sales_order.cust_id )FROM sales_orderWHERE order_date > '1994/01/01'ORDER BY order_date
The subquery refers to the cust_id column in the sales_order table even though the sales_order table is not part of the subquery. Instead, the sales_order.cust_id column refers to the sales_order table in the main body of the statement. This is called an outer reference. Any subquery that contains an outer reference is called a correlated subquery.
A subquery can be used instead of a join whenever only one column is required from the other table. (Recall that subqueries can only return one column.) In this example, you only needed the company_name column so the join could be changed into a subquery.
If the subquery might have no result, this method is called an outer join. The join in previous sections of the tutorial is more fully called an inner join.
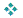 To list all customers in Washington State together with their most recent order ID:
To list all customers in Washington State together with their most recent order ID:
SELECT company_name, state,( SELECT MAX( id )FROM sales_orderWHERE sales_order.cust_id = customer.id )FROM customerWHERE state = 'WA'
| company_name | MAX(id) | state |
|---|---|---|
| Custom Designs | 2547 | WA |
| It's a Hit! | (NULL) | WA |
The It's a Hit! company placed no orders, and the subquery returns NULL for this customer. Companies who have not placed an order would not be listed if an inner join was used.
You could also specify an outer join explicitly. In this case a GROUP BY clause is also required.
SELECT company_name,MAX( sales_order.id ),stateFROM customerKEY LEFT OUTER JOIN sales_orderWHERE state = 'WA'GROUP BY company_name, state